This page is part of the dwv architecture description and describes the dwv load process.
Summary:
Load classes
Data can come from 3 types of source: url (via a XMLHttpRequest), file (via a FileReader) or directly as a memory buffer. The 3 'meta' loaders responsible for each source are: UrlsLoader, FilesLoader and MemoryLoader.
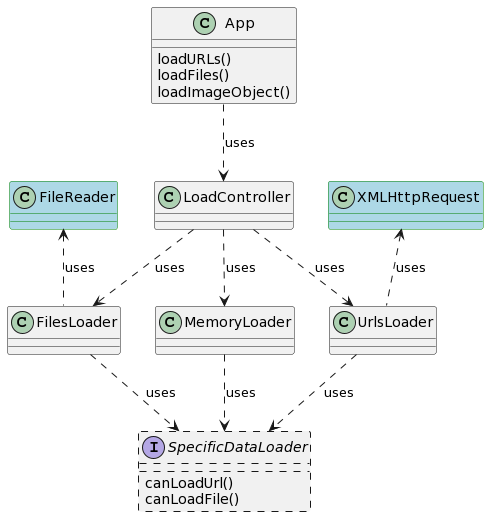
Classes involved in the load process.
Each 'meta' loader retrieves the data and passes it to a specialised loader according to its answer to the canLoadUrl or canLoadFile call. Specialised loaders will typically convert the binary retrieved data into a local class, for example an Image.
The current specialised loaders are:
- DicomDataLoader: for DICOM data
- JSONTextLoader: for JSON data
- RawImageLoader: for image formats supported by the browser
- RawVideoLoader: for video formats supported by the browser
- ZipLoader: for data compressed in a ZIP file
The main specialised loader, the DicomDataLoader, parses the binary dicom file to extract all the meta data and then creates an Image, at first with only one slice. When multiple items are loaded, it will append the extracted data to the first image to create a multi slice image. Note that the dicom image data can be stored in a compressed format, in that case the DICOM loader will decompress the data to create the image.
Load sequence
Here are the events triggered during the complete load process (meaning the load of all the items):
loadstart: the load started!loadprogress: the progress of the complete load (all items),loaditem: an item finished loading, an item can be a url or a file,load: all items were loaded successfully,error: an error has occured during load,abort: the load process has been aborted,loadend: the process has completed, whether successfully (afterload) or unsuccessfully (afterabortorerror).
Once the load is started a unique dataId (string) is associated to the data being loaded.
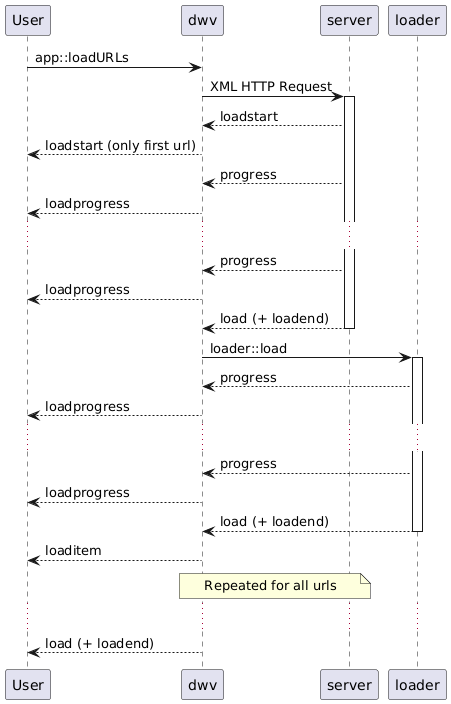
Example successful load sequence for loading a list of urls.